Saturday 29 December 2007
Vista : The great disk hog!
Manual tips for reclaiming space
Vista System Junk Cleaner tool
Friday 21 December 2007
SPN - Service Principal Name Registration
We need a SPN established to allow Kerberos authentication with SQL.
Kerberos allows pass through authentication eg user > web server > sql server
You want to create an spn for a sql instance when the account that sql server runs from does not have rights to create an SPN (most cases really, in secure environments).
To manually configure an SPN you need 'setspn', which is part of 'Windows 2000 / 2003 Resource Kit'. Once installed >
C:\Program Files\Resource Kit>setspn
Usage: setspn [switches data] computername Where "computername" can be the name or domain\name
Switches: -R = reset HOST ServicePrincipalName Usage: setspn -R computername
-A = add arbitrary SPN Usage: setspn -A SPN computername
-D = delete arbitrary SPN Usage: setspn -D SPN computername
-L = list registered SPNs Usage: setspn [-L] computername
Examples:
setspn -R daserver1 It will register SPN "HOST/daserver1" and "HOST/{DNS of daserver1}"
setspn -A http/daserver daserver1 It will register SPN "http/daserver" for computer "daserver1"
setspn -D http/daserver daserver1 It will delete SPN "http/daserver" for computer "daserver1"
Adding a SPN > setspn - A SERVICENAME/FQDN serviceaccount
C:\Program Files\Resource Kit>setspn -A MSSQLSvc/livesql001.domain.co.uk SqlServiceAccount
Registering ServicePrincipalNames for CN=SqlServiceAccount,OU=Service Accounts,DC=domain,DC=co,DC=uk MSSQLSvc/livesql001.domain.co.uk Updated object
C:\Program Files\Resource Kit>setspn -A MSSQLSvc/livesql001.domain.co.uk:1433 SqlServiceAccount Registering ServicePrincipalNames for CN=SqlServiceAccount,OU=Service Accounts,DC=domain,DC=co,DC=uk MSSQLSvc/livesql001.domain.co.uk:1433 Updated object
Checking an SPN > setspn -l serviceaccount
C:\Program Files\Resource Kit>setspn -l SqlServiceAccount
Registered ServicePrincipalNames for CN=SqlServiceAccount,OU=Service Accounts,DC=domain,DC=co,DC=uk: MSSQLSvc/livesql001.domain.co.uk:1433 MSSQLSvc/livesql001.domain.co.uk MSSQLSvc/livesql002.domain.co.uk:1433 MSSQLSvc/testsql002.domain.co.uk:1433 MSSQLSvc/livesql002:1433 MSSQLSvc/devsql001.domain.co.uk:1433
You can also check an spn via adsi edit (Active Directory editor tool).
Technet explanation on SPNs >
http://technet2.microsoft.com/windowsserver/en/library/8127f5ed-4e05-4822-bfa9-402ceede47441033.mspx?mfr=true
So, SPN ties together -
- machine name
- port number
- account name
Friday 14 December 2007
Grant Execute to all Stored Procedures
SELECT 'GRANT EXECUTE ON ' + NAME + ' TO LoginName' -- Replace LoginName with the name of your new Login FROM SYSOBJECTS WHERE TYPE = 'P' AND LEFT(NAME,2) <> 'sp' -- system procs AND LEFT(NAME,2) <> 'dt' -- VSS procs
Solution 2 : Procedure -
CREATE PROCEDURE USP_gen_CreateGrants AS DECLARE @ExecSQL varchar(100) DECLARE curGrants CURSOR FOR SELECT 'GRANT EXECUTE ON ' + NAME + ' TO MyLogin' -- Replace MyLogin with the name of your new Login FROM SYSOBJECTS WHERE TYPE = 'P' AND LEFT(NAME,2) <> 'sp' -- system procs AND LEFT(NAME,2) <> 'dt' -- VSS procs OPEN curGrants FETCH NEXT FROM curGrants INTO @ExecSQL WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN Exec(@ExecSQL) IF @@ERROR <> 0 BEGIN RETURN 1 -- return 1 if there is an error END Print @ExecSQL FETCH NEXT FROM curGrants INTO @ExecSQL END CLOSE curGrants DEALLOCATE curGrants
Sunday 9 December 2007
SQL Server Default Port Numbers
1433 – SQL Server
1434 – SQL Browser
2383 – Analysis Services
4022 – Service Broker
Useful tool : WindirStat

A funky tool to help visualise and hence clean up hard disk bloat. It proved very helpful in finding over 5GB of rubbish left in c:\windows\csc by a colleague who used 'Client Side Caching'.
The application even features an animated Pacman character during disk analysis :)
Download it for free @ http://windirstat.info/
Saturday 8 December 2007
Blogger : Feeling Lucky Widget
I've implemented it over there on the right >>>
http://phydeauxredux.googlepages.com/Blogger-Feeling-Lucky.html
Monday 3 December 2007
Datetime manipulation Gotcha
SELECT CONVERT(DATETIME,'2007-12-03 11:51:00.000',21)
2007-12-03 11:51:00.000
PRINT CONVERT(DATETIME,'2007-12-03 11:51:00.000',21)
Dec 3 2007 11:51AM
Friday 30 November 2007
SSIS : The semaphore timeout period has expired
Some SSIS load packages failed this morning >
Error 121: "The semaphore timeout period has expired" (ERROR_SEM_TIMEOUT).
There is no one answer to this except to say that is a tcp/ip networking error.
Newsgroup posts on the issue range from antivirus software, network congestion and black hole routers. If anyone can be less vague, i'd love to hear your thoughts.
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/325487
Wednesday 21 November 2007
DMV Performance Counters - Buffer Cache hit ratio example
Returns a single value, i.e. the buffer cache hit ratio.
This represents how well pages stay in buffer cache.
The closer the result is to 100%, the better.
Corrected from version here
This version -
- includes the necessary join
- will run on any server (wildcarded the server name)
SELECT (a.cntr_value * 1.0 / b.cntr_value) * 100.0 [BufferCacheHitRatio]
FROM (SELECT *, 1 x
FROM sys.dm_os_performance_counters
WHERE counter_name = 'Buffer cache hit ratio'
AND object_name like '%:Buffer Manager%') a
JOIN
(SELECT *, 1 x
FROM sys.dm_os_performance_counters
WHERE counter_name = 'Buffer cache hit ratio base'
AND object_name like '%Buffer Manager%') b
ON a.x = b.x
Tuesday 13 November 2007
Examining SQL Column types (2005+)
select o.type_desc, o.name, c.name, t.name , c.max_length, c.precision from sys.columns c inner join sys.types t on c.system_type_id = t.system_type_id inner join sys.objects o on c.object_id = o.object_id where o.type_desc not like 'system%' and o.type_desc not like 'int%' order by 1,2,3,4
Saturday 10 November 2007
TSQL : Agent Job Notififications via email
1) Set Sql agent to use a database mail profile.
-- Set default database mail profile for sql agent -- My dbamail profile name is 'SQL Operator' USE [msdb] GO EXEC master.dbo.xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', N'SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\SQLServerAgent', N'DatabaseMailProfile', N'REG_SZ', N'SQL Operator' GO
2) Add an operator (email recipient) for the alerts.
-- Add Operator Recipient for Sql Agent jobs USE [msdb] GO EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_operator @name=N'Agent Job Operator', @enabled=1, @pager_days=0, @email_address=N'dba@mydomain.co.uk' GO
3) Set the jobs to send emails on failure.
USE [msdb] GO sp_update_job select 'exec sp_update_job @job_name = '''+name+''' , @notify_email_operator_name = ''Agent Job Operator'' , @notify_level_email = 2' from msdb.dbo.sysjobs where enabled = 1 /* note values for @notify_level_email signify when to send emails are - 0 - never 1 - success 2 - failure 3 - always */
Moving TempDB / Splitting TempDB to multiple files
You need to restart SQL for tempdb to be recreated in the new locations...
USE master GO -- move tempdb data ALTER DATABASE tempdb MODIFY FILE (NAME = tempdev, FILEGROWTH = 10% , MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED, SIZE=1000MB , FILENAME = 'D:\databases\tempdb_1.mdf') GO -- move tempdb log ALTER DATABASE tempdb MODIFY FILE (NAME = templog, SIZE=1, FILENAME = 'D:\databases\templog.ldf') GO -- additional processor? split tempdb into equal filesizes, 1 per processor... ALTER DATABASE tempdb ADD FILE (NAME = tempdev_2, FILEGROWTH = 10% , MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED, SIZE=1000MB , FILENAME = 'D:\databases\tempdb_2.mdf') GO
Wednesday 7 November 2007
Configuring Event Forwarding - All events
USE msdb go EXEC master.dbo.sp_MSsetalertinfo @forwardingserver=N'test', @forwardalways=1, @forwardingseverity=10 go
Saturday 3 November 2007
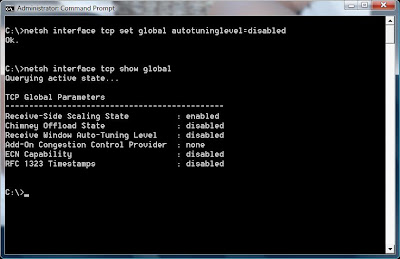
Vista : Disable TCP Window Scaling
The trouble is, not many hosts support it and some routers also dont like it.
The end result is people experiencing slow networking on Vista.
Turn it off like this (from Administrator command prompt) >
netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled
Check the status like this >
netsh interface tcp show global
A nice pretty screenshot >
Fast Row Counts
-- fast row counts
SELECT
S.name as schemaname,
T.name as tablename,
P.rows
FROM sys.partitions P
INNER JOIN sys.tables T ON P.object_Id = T.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.schemas S ON T.schema_id = S.schema_id
WHERE P.index_id IN (0,1)
ORDER BY 1,2
Friday 2 November 2007
USP_EffectiveLoginPermissions
Create the Procedure in master db or your tools database.
EXEC USP_EffectiveLoginPermissions '' go
CREATE PROCEDURE USP_EffectiveLoginPermissions
@User VARCHAR(100)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##ServerLogins') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##SERVERLOGINS
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##DBUsers') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##DBUSERS
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##DBList') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##DBLIST
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##Results') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##RESULTS
END
DECLARE @DBName VARCHAR(128);
DECLARE @SQLCmd VARCHAR(2000);
DECLARE @NumberOfDBs INT;
-- Get the SQL Server logins
-- Create login table
CREATE TABLE ##SERVERLOGINS (
[SID] VARBINARY(85) NULL,
[LOGIN_NAME] VARCHAR(128) NULL);
-- Populate login table
INSERT INTO ##SERVERLOGINS
SELECT SID,CAST(LOGINNAME AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [LOGIN_NAME]
FROM MASTER.DBO.SYSLOGINS
-- Create list of databases
CREATE TABLE ##DBLIST (
[DBNAME] VARCHAR(128))
-- perform for all dbs on server
INSERT INTO ##DBLIST
SELECT [NAME]
FROM MASTER..SYSDATABASES
WHERE [DBID] > 4
ORDER BY [NAME];
SELECT @NumberOfDBs = COUNT(* )
FROM ##DBLIST
-- Create the output table for the Database User ID's
CREATE TABLE ##DBUSERS (
[DATABASE_USER_ID] VARCHAR(128),
[SERVER_LOGIN] VARCHAR(128),
[DATABASE_ROLE] VARCHAR(128),
[DATABASE_NAME] VARCHAR(128));
-- Declare a cursor to loop through all the databases on the server
DECLARE CSRDB CURSOR FOR
SELECT [DBNAME]
FROM ##DBLIST
ORDER BY [DBNAME]
-- Open the cursor and get the first database name
OPEN CSRDB
FETCH NEXT FROM CSRDB
INTO @DBName
-- Loop through the cursor
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- populate ##DBUsers table for current db
SELECT @SQLCmd = 'INSERT ##DBUsers '
+ ' SELECT CAST(su.[name] AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [database_user_id], '
+ ' CAST(COALESCE (u.[login_name], ''* Orphaned *'') AS VARCHAR(128))AS [server_login], '
+ ' CAST(COALESCE (sug.name, ''Public'') AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [database_role],'
+ ' CAST(''' + @DBName + ''' AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [database_name]'
+ ' FROM [' + @DBName + '].[dbo].[sysusers] su'
+ ' LEFT OUTER JOIN ##ServerLogins u' + ' ON su.sid = u.sid'
+ ' LEFT OUTER JOIN ([' + @DBName + '].[dbo].[sysmembers] sm '
+ ' INNER JOIN [' + @DBName + '].[dbo].[sysusers] sug '
+ ' ON sm.groupuid = sug.uid)'
+ ' ON su.uid = sm.memberuid '
+ ' WHERE su.hasdbaccess = 1'
IF LTRIM(RTRIM(@User)) <> ''
SELECT @SQLCmd = @SQLCmd + ' AND SU.name = ''' + @User + ''''
-- uncomment to debug
-- PRINT @SQLCmd
EXEC(@SQLCmd)
-- Get the next database name
FETCH NEXT FROM CSRDB
INTO @DBName
-- End of the cursor loop
END
-- Close and deallocate the CURSOR
CLOSE CSRDB
DEALLOCATE CSRDB
CREATE TABLE ##RESULTS (
[INSTANCE_NAME] VARCHAR(128),
[DATABASE_NAME] VARCHAR(128),
[OBJTYPE] VARCHAR(128),
[LOGIN_STATUS] VARCHAR(128),
[USERGRANTEE] VARCHAR(128));
TRUNCATE TABLE ##RESULTS
--data for logins
INSERT INTO ##RESULTS
SELECT
CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)) AS INSTANCE_NAME,
DATABASE_NAME,
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_datareader' THEN 'db_datareader, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_accessadmin' THEN 'db_accessadmin, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_backupoperator' THEN 'db_backupoperator, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_datawriter' THEN 'db_datawriter, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_ddladmin' THEN 'db_ddladmin, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_denydatareader' THEN 'db_denydatareader, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_denydatawriter' THEN 'db_denydatawriter, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_owner' THEN 'db_owner, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_securityadmin' THEN 'db_securityadmin, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'public' THEN 'public, ' ELSE '' END) AS ROLE_OBJECTTYPE,
CASE [SERVER_LOGIN] WHEN '* Orphaned *' THEN [SERVER_LOGIN] ELSE 'OK' END AS LOGIN_STATUS,
CASE WHEN [DATABASE_USER_ID] = [SERVER_LOGIN] THEN [DATABASE_USER_ID]
WHEN [SERVER_LOGIN] = '* Orphaned *' THEN [DATABASE_USER_ID]
ELSE [DATABASE_USER_ID] + ' (' + [SERVER_LOGIN] + ')' END AS USER_GRANTEE
FROM
##DBUSERS
GROUP BY
[DATABASE_NAME],
[DATABASE_USER_ID],
[SERVER_LOGIN]
SELECT
[INSTANCE_NAME],
[DATABASE_NAME],
[USERGRANTEE],
LEFT(OBJTYPE,LEN([OBJTYPE])-1) AS ROLES,
[LOGIN_STATUS]
FROM
##RESULTS
ORDER BY
1, 2, 3
END
go
Thursday 1 November 2007
USP_EffectivePermissions
Usage : EXEC USP_EffectivePermissions 'username'
Install in master db to use from any db on the server.
CREATE PROC USP_EffectivePermissions
@User VARCHAR(100)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##ServerLogins') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##SERVERLOGINS
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##DBUsers') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##DBUSERS
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##DBList') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##DBLIST
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##DBObjPermissions') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##DBOBJPERMISSIONS
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##CrossJoinMultiplier') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##CROSSJOINMULTIPLIER
END
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..##Results') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE ##RESULTS
END
DECLARE @DBName VARCHAR(128);
DECLARE @SQLCmd VARCHAR(2000);
DECLARE @NumberOfDBs INT;
-- Get the SQL Server logins
-- Create login table
CREATE TABLE ##SERVERLOGINS ([SID] VARBINARY(85) NULL,[LOGIN_NAME] VARCHAR(128) NULL);
-- Populate login table
INSERT INTO ##SERVERLOGINS
SELECT SID,CAST(LOGINNAME AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [LOGIN_NAME]
FROM MASTER.DBO.SYSLOGINS
WHERE LOGINNAME = @User;
-- Create list of databases
CREATE TABLE ##DBLIST (
[DBNAME] VARCHAR(128))
-- perform for all dbs on server
INSERT INTO ##DBLIST
SELECT NAME
FROM MASTER..SYSDATABASES
WHERE DBID > 4
ORDER BY NAME;
SELECT @NumberOfDBs = COUNT(* )
FROM ##DBLIST
-- Create the output table for the Database User ID's
CREATE TABLE ##DBUSERS (
[DATABASE_USER_ID] VARCHAR(128),
[SERVER_LOGIN] VARCHAR(128),
[DATABASE_ROLE] VARCHAR(128),
[DATABASE_NAME] VARCHAR(128));
-- Create the output table for Object Level Permissions
CREATE TABLE ##DBOBJPERMISSIONS (
[DATABASE_NAME] VARCHAR(128),
[GRANTOR] VARCHAR(128),
[GRANTEE] VARCHAR(128),
[OBJTYPE] VARCHAR(128),
[OBJECTNAME] VARCHAR(128),
[PERMISSION_LEVEL] VARCHAR(128),
[PERMISSION] VARCHAR(128));
-- Declare a cursor to loop through all the databases on the server
DECLARE CSRDB CURSOR FOR
SELECT DBNAME
FROM ##DBLIST
ORDER BY DBNAME
-- Open the cursor and get the first database name
OPEN CSRDB
FETCH NEXT FROM CSRDB
INTO @DBName
-- Loop through the cursor
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- populate ##DBUsers table for current db
SELECT @SQLCmd = 'INSERT ##DBUsers '
+ ' SELECT CAST(su.[name] AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [database_user_id], '
+ ' CAST(COALESCE (u.[login_name], ''* Orphaned *'') AS VARCHAR(128))AS [server_login], '
+ ' CAST(COALESCE (sug.name, ''Public'') AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [database_role],'
+ ' CAST(''' + @DBName + ''' AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [database_name]'
+ ' FROM [' + @DBName + '].[dbo].[sysusers] su'
+ ' LEFT OUTER JOIN ##ServerLogins u' + ' ON su.sid = u.sid'
+ ' LEFT OUTER JOIN ([' + @DBName + '].[dbo].[sysmembers] sm '
+ ' INNER JOIN [' + @DBName + '].[dbo].[sysusers] sug '
+ ' ON sm.groupuid = sug.uid)'
+ ' ON su.uid = sm.memberuid '
+ ' WHERE su.hasdbaccess = 1'
+ ' AND SU.name = ''' + @User + ''''
-- uncomment to debug
-- PRINT @SQLCmd
EXEC(@SQLCmd)
-- populate ##DBObjPermissions table for current db
SELECT @SQLCmd = 'use [' + @DBName + '];'
+ 'insert into ##DBObjPermissions '
+ ' select '
+ ' CAST(''' + @DBName + ''' AS VARCHAR(128)) AS [database_name],'
+ ' user_name(sec.grantor) as grantor, '
+ ' user_name(sec.uid) as grantee, '
+ ' case obj.type '
+ ' when ''C'' then ''Check constraint'' '
+ ' when ''D'' then ''Default (constraint or stand-alone)'' '
+ ' when ''F'' then ''Foreign Key'' '
+ ' when ''PK'' then ''Primary Key'' '
+ ' when ''P'' then ''Stored Procedure'' '
+ ' when ''FN'' then ''Function (Scalar)'' '
+ ' when ''IF'' then ''Function (Inline)'' '
+ ' when ''R'' then ''Rule (old-style, stand-alone)'' '
+ ' when ''RF'' then ''Replication-filter-procedure'' '
+ ' when ''S'' then ''System base table'' '
+ ' when ''TA'' then ''Assembly (CLR) DML trigger'' '
+ ' when ''TF'' then ''Function (TableValued)'' '
+ ' when ''U'' then ''Table'' '
+ ' when ''UQ'' then ''Unique constraint'' '
+ ' when ''V'' then ''View'' '
+ ' when ''X'' then ''Extended stored procedure'' '
+ ' end as objtype, '
+ ' stbl.name + ''.'' + obj.name as objectname, '
+ ' protecttype.name permission_level, ' + ' action.name as permission '
+ ' from ' + '[' + @DBName + '].dbo.sysobjects as obj '
+ ' inner join [' + @DBName + '].dbo.sysusers as stbl on stbl.uid = obj.uid '
+ ' and stbl.name = ''' + @User + ''''
+ ' inner join ##DBUsers on ##DBUsers.[database_user_id] COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CS_AS = stbl.name COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CS_AS'
+ ' inner join [' + @DBName + '].dbo.sysprotects as sec on sec.id = obj.id '
+ ' inner join master.dbo.spt_values as action on sec.action = action.number and action.type = ''t'' '
+ ' inner join master.dbo.spt_values as protecttype on sec.protecttype = protecttype.number and protecttype.type = ''t'' '
+ ' where objectpropertyex(obj.id,''ismsshipped'') = 0 '
-- uncomment to debug
-- PRINT @SQLCmd
EXEC(@SQLCmd)
-- Get the next database name
FETCH NEXT FROM CSRDB
INTO @DBName
-- End of the cursor loop
END
-- Close and deallocate the CURSOR
CLOSE CSRDB
DEALLOCATE CSRDB
CREATE TABLE ##CROSSJOINMULTIPLIER (
USERNAME VARCHAR(128) NULL);
IF @NumberOfDBs = 1
INSERT INTO ##CROSSJOINMULTIPLIER
SELECT [SERVER_LOGIN]
FROM ##DBUSERS -- 1 db, multiply section headers by users
ELSE
INSERT INTO ##CROSSJOINMULTIPLIER
SELECT TOP 1 'dummy'
FROM SYSOBJECTS -- multiple dbs,
CREATE TABLE ##RESULTS (
[HEADER_ROW] INT,[DATABASE_NAME] VARCHAR(128),[SORT_ORDER] INT,[GRANTOR] VARCHAR(128),[GRANTEE] VARCHAR(128),[OBJTYPE] VARCHAR(128),[OBJECTNAME] VARCHAR(128),[USERGRANTEE] VARCHAR(128),[PERMISSION_LEVEL] VARCHAR(128),[PERMISSION] VARCHAR(128));
TRUNCATE TABLE ##RESULTS
--data for logins
INSERT INTO ##RESULTS
SELECT
0 AS HEADER_ROW,
CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)) + ' - ' + DATABASE_NAME AS DATABASE_NAME,
2 AS SORT_ORDER,
'' AS GRANTOR,
'' AS GRANTEE,
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_datareader' THEN 'db_datareader, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_accessadmin' THEN 'db_accessadmin, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_backupoperator' THEN 'db_backupoperator, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_datawriter' THEN 'db_datawriter, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_ddladmin' THEN 'db_ddladmin, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_denydatareader' THEN 'db_denydatareader, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_denydatawriter' THEN 'db_denydatawriter, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_owner' THEN 'db_owner, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'db_securityadmin' THEN 'db_securityadmin, ' ELSE '' END) +
MAX(CASE [DATABASE_ROLE] WHEN 'public' THEN 'public, ' ELSE '' END) AS ROLE_OBJECTTYPE,
'database user' AS OBJ_NAME,
CASE [SERVER_LOGIN] WHEN [DATABASE_USER_ID] THEN [DATABASE_USER_ID] ELSE [DATABASE_USER_ID] + ' (' + [SERVER_LOGIN] + ')' END AS USER_GRANTEE,
'' AS PERMISSION_LEVEL,
'' AS PERMISSION
FROM
##DBUSERS
GROUP BY
[DATABASE_NAME],
[DATABASE_USER_ID],
[SERVER_LOGIN]
-- data for objects
INSERT INTO ##RESULTS
SELECT 0 AS HEADER_ROW,
CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)) + ' - ' + DATABASE_NAME AS DATABASE_NAME,
4 AS SORT_ORDER,
GRANTOR,
GRANTEE,
[OBJTYPE] AS ROLE_OBJECTTYPE,
[OBJECTNAME] AS OBJ_NAME,
[GRANTEE] AS USER_GRANTEE,
[PERMISSION_LEVEL] AS PERMISSION_LEVEL,
[PERMISSION] AS PERMISSION
FROM ##DBOBJPERMISSIONS
INSERT INTO ##RESULTS
SELECT 1 AS HEADER_ROW,
CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)) + ' - ' + DBNAME AS DATABASE_NAME,
1 AS SORT_ORDER,
'' AS GRANTOR,
'' AS GRANTEE,
'Role' AS ROLE_OBJECTTYPE,
'Object' AS OBJ_NAME,
'User' AS USER_GRANTEE,
' ' AS PERMISSION_LEVEL,
' ' AS PERMISSION
FROM ##DBLIST
INNER JOIN ##RESULTS
ON ##RESULTS.DATABASE_NAME = CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)) + ' - ' + ##DBLIST.DBNAME
AND ##RESULTS.SORT_ORDER = 2
-- header rows for objects
INSERT INTO ##RESULTS
SELECT 1 AS HEADER_ROW,
CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)) + ' - ' + DBNAME AS DATABASE_NAME,
3 AS SORT_ORDER,
'' AS GRANTOR,
'' AS GRANTEE,
'Object Type' AS ROLE_OBJECTTYPE,
'Object' AS OBJ_NAME,
'Grantee' AS USER_GRANTEE,
'Permission Level' AS PERMISSION_LEVEL,
'Permission' AS PERMISSION
FROM ##DBLIST
INNER JOIN ##RESULTS
ON ##RESULTS.DATABASE_NAME = CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)) + ' - ' + ##DBLIST.DBNAME
AND ##RESULTS.SORT_ORDER = 4
SELECT
DATABASE_NAME,
GRANTOR,
GRANTEE,
OBJTYPE,
OBJECTNAME,
USERGRANTEE,
PERMISSION_LEVEL,
PERMISSION
FROM
##RESULTS
ORDER BY
DATABASE_NAME,
SORT_ORDER
END
go
Sunday 28 October 2007
Windows Installer Cleanup Utility
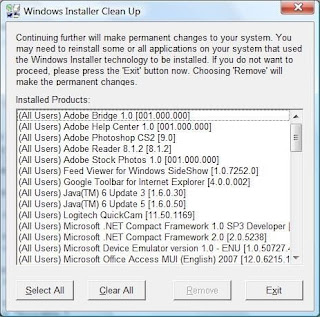
As someone familiar with repairing installer issues manually, I was surprised to find they had issued a tool to help. Windows Installer Cleanup Utility crucialy zaps the files in the c:\windows\installer directory for the application you chose and removes registry entries so you can restart a failed installation.
1) Download & Install from http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;290301
2) Run from 'start > all programs > windows install cleanup'
3) Select the program you wish to cleanup.
Tuesday 23 October 2007
Vista : Where is telnet?
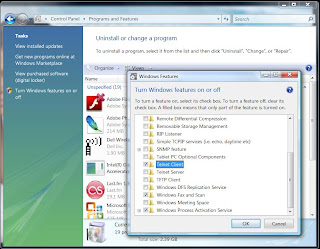
1) Start > Control Panel > Programs and Features
2) Look on left hand task pane and click 'Turn Windows Features on or off'
3) Locate and enable 'Telnet Client' in the list that appears.
4) Click OK and wait (for what seems like an eon)
Proceed to command prompt and use telnet like in the good old days :)
Saturday 20 October 2007
Vista System Restore - Disk Space Hog
1) Open Administrative Command prompt for dos prompt
2) vssadmin list shadowstorage [enter]
< Results show disk space reserved for Vista System Restore >
Given the default is 15% of drive capacity, you'll probably want to change this....
3) vssadmin Resize ShadowStorage /For=[drive letter]: /On=[drive letter]: /MaxSize=[space] [enter]
e.g. vssadmin Resize ShadowStorage /For=C: /On=C: /MaxSize=1GB
< Should get message saying success, or error if you get it wrong! >
4) use first command to confirm new setting >
vssadmin list shadowstorage [enter]
Wednesday 17 October 2007
Thursday 11 October 2007
Lose a bloaty Transaction Log file
-- find logical name of log file SELECT * FROM sys.sysfiles -- Change recovery model to SIMPLE. ALTER DATABASE DATABASE_NAME SET RECOVERY SIMPLE -- Shrink truncated log file to 1 MB. DBCC SHRINKFILE (data_log, 1); GO -- Change recovery model to FULL. ALTER DATABASE DATABASE_NAME SET RECOVERY FULL !!! Take FULL backup as your chain of Transaction log backups will now be broken by the RECOVERY mode change.
Tuesday 9 October 2007
Importing Trace files back into SQL
select * into ServerSideTraceData
from fn_trace_gettable('C:\tracedata\2007-09-09.trc', 3);
-- use default flag to import all files.
select * into ServerSideTraceData
from fn_trace_gettable('C:\tracedata\2007-09-09.trc', default);
http://blogs.msdn.com/microsoft_dynamics_nav_sustained_engineering/archive/2007/10/19/diagnose-your-sql-server.aspx
Friday 5 October 2007
Datawarehousing Notes
A fact could contain raw data or aggregated data with quantifiable measures.
Measures are numerical values defined by the granularity of the fact.
The ‘grain’ represents the unit at which information is stored and defines the type of the fact.
(1) Transactional
Data is stored at the transaction level, typically with little manipulation from the source OLTP system except cleanup and assigning of keys.
(2) Periodic Snapshot
Data is a picture of what happened at a moment in time i.e. more rows are added as time passes.
(3) Accumulating Snapshot
Data record is amended over time e.g. for an hourly sales fact, the data record would be updated during the hour real time transactions were occurring.
Fact tables have many rows and fewer columns when compared to dimensions.

A fact is uniquely identified by a set of foreign keys (linking to dimension tables). The primary key of a fact may be some or all of the foreign keys.
Fact Examples
Sales Transactions, Website Visitor Sessions
Dimension
A dimension is a table representing a category by which we organize facts.
They provide labeling, grouping and filtering functionality.
It is made up of attributes, the combinations of which represent a unique level of data within a dimension.
Dimension tables should have many attributes and typically less rows than related fact tables.
Dimensions are independent of one another.
To query multiple dimensions, you join through fact tables.
A dimension used by multiple facts is known as a Conformed Dimension.
There are 3 types of dimension, defined by the way data updates are handled >
Type 1
Data changes replace the existing row. No record of the previous attribute values exist.
‘Address’ is a good example as storing old address details serves little use.
Type 2
Data changes are added to the table as a new row. Therefore the history of attribute values are stored. ‘Interest Rate’ is an example where the history is important.
Type 3
Data changes overwrite the attribute values, but the old values are stored in additional columns in the dimension. Only 1 level of history can be retrieved therefore.
Dimension Examples
Calendar, Customer List, Product List
Monster Dimensions
An extremely large Dimension needs to be divided for the sake of performance.
Examples of this are >
1) splitting a calendar dimension into separate Date and Time dimensions on account of it’s shear size.
2) splitting a customer dimension out into 2 dimensions for mostly static and changeable data respectively.
Junk Dimensions
These are a way of storing commonly used flags (y/n) and indicators that have a low number of possible values. It is a tidier solution to store them centrally, rather than create clutter i.e numerous small dimensional tables.
Nulls
Nulls have no place in a data warehouse.
To cope for null values in dimensions, implement an ‘Unknown Value’ row in dimensions and ensure foreign keys in facts point to it.
-1 is a suggested primary key value for the Unknown data row.
Keys
Natural Key
A Natural key is a meaningful value.
For example, a National Insurance (NI) number uniquely identifies employees in the UK
Surrogate Key
This is a sequential number assigned to records.
Primary and Foreign keys in data warehouse designs should use surrogate values.
Wednesday 3 October 2007
USP_TableScript
CREATE PROCEDURE USP_TableScript
@TableName varchar(100),
@NewTableName varchar(100),
@RetainNulls int,
@TableDef varchar(max) OUTPUT
AS
/*
USP_TableScript
Paramters : 'originaltable' , 'newtablename', 0/1 - retain null settings, output variable
*/
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_NAME = @tableName)
Begin
declare @sql varchar(8000)
declare @table varchar(100)
declare @cols table (datatype varchar(50))
insert into @cols values('bit')
insert into @cols values('binary')
insert into @cols values('bigint')
insert into @cols values('int')
insert into @cols values('float')
insert into @cols values('datetime')
insert into @cols values('text')
insert into @cols values('image')
insert into @cols values('uniqueidentifier')
insert into @cols values('smalldatetime')
insert into @cols values('tinyint')
insert into @cols values('smallint')
insert into @cols values('sql_variant')
set @sql=''
Select @sql=@sql+
case when charindex('(',@sql,1)<=0 then '(' else '' end +Column_Name + ' ' +Data_Type + case when Data_Type in (Select datatype from @cols) then '' else '(' end+ case when Data_type in ('real','money','decimal','numeric') then cast(isnull(numeric_precision,'') as varchar)+','+ case when Data_type in ('real','money','decimal','numeric') then cast(isnull(Numeric_Scale,'') as varchar) end when Data_type in ('char','nvarchar','varchar','nchar') then cast(isnull(Character_Maximum_Length,'') as varchar) else '' end+ case when Data_Type in (Select datatype from @cols)then '' else ')' end+ case when (@RetainNulls = 1 AND Is_Nullable='NO') then ' NOT NULL,' + CHAR(10) else ' NULL,' + CHAR(10) end from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where Table_Name=@tableName select @table= 'CREATE TABLE [' + @NewTableName + '] ' from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where table_Name=@tableName select @sql=@table + substring(@sql,1,len(@sql)-2) +' )' select @TableDef = replace(@sql,'()','') End go
Usage ;
DECLARE @SQLSTRING NVARCHAR(MAX) EXEC USP_TableScript 'Contact','##temp_Contact', 0,@SQLSTRING OUTPUT EXEC sp_executesql @SQLSTRING
Tuesday 25 September 2007
Configuring Certificate for MSX (Master/Target Server Environment)
1) Install Certificate. - Import .pfx file provided by operations onto the sql server.
#1.1 - double click pfx file to begin certificate import. wizard will confirm file name. click 'next' to confirm
#1.2 - provide private key password, click next
#1.3 - select 'place certificates in following store' , select 'personal' , OK
#1.4 - click next on confirmation page, 'hopefully recieve the message - 'the import was successful'
2) Associate the certificate with sql instance
#2.1 - start > run > regedit {enter]
#2.2 - Use Regedit to navigate the registry to >
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\
Set MsxEncryptChannelOptions(REG_DWORD) to 2
Useful Links
Troubleshooting MSX >
http://blogs.ameriteach.com/chris-randall/2007/8/23/sql-server-2005-troubleshooting-multi-server-administration-.html
setting encryption options on target servers >
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms365379.aspx
configuring certificate for use by ssl (by mmc) >
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/316898
configuring certificate for use by ssl (commands) >
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186362.aspx
Wednesday 12 September 2007
JDBC v1.2 Application connectivity issue
Steps taken -
- sql traces performed (stored procedure was being executed against db)
- sp returns data (proved this by running the traced code manually in a query window)
- became puzzled...
Solution - SQLServerException: The statement did not return a result set when sp uses cursors
The Java code was using executeQuery rather than execute . This meant that executeQuery was effectively seeing 'inside' the stored procedure and was looking at a recordset in use by a cursor, rather than the final recordset returned when the query was run manually.
"The method executeQuery is designed for statements that produce a single result set, such as SELECT statements"
"The method execute is used to execute statements that return more than one result set, more than one update count, or a combination of the two."
http://forums.microsoft.com/MSDN/ShowPost.aspx?PostID=1710309&SiteID=1
Tuesday 11 September 2007
JDBC connecting to a named instance of sql 2005
JdbcURL=jdbc:sqlserver://RIO:2433;instanceName=SQL2005;databaseName=Statistics
(i needed this when an application was provided to us and the ISV had not heard of a 'named instance' before :)
Sunday 9 September 2007
Common UK DateTime Formats
SELECT CONVERT(varchar(10), getdate() , 103)
09/09/2007
SELECT CONVERT(varchar(10), getdate() , 120)
2007-09-09
SELECT CONVERT(varchar(20), getdate() , 120)
2007-09-09 12:18:29
strip non-numeric characters (e.g to use datetime in a filename) -
SELECT REPLACE(REPLACE(REPLACE(CONVERT(varchar(20), getdate() , 120),'-',''),' ',''),':','')
20070909123203
Thursday 30 August 2007
Login Failures : Blank Username
This occurs on own or in conjuction with other errors , e.g. SSPI.
Bottom line is that it is a Windows Authentication error.
Therefore, nag the networks team or get stuck in with debugging yourself...
Wednesday 29 August 2007
Statistics Options
AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS
On by default on a new database, it means index and column statistics are updated 'on the fly'.
AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS_ASYNC
Queries are run against the current statistics, rather than waiting fot them to be updated first.
The statistics are triggered to be updated asap, hopefully in time for the next query.
I havent (yet) found a system where index updates futher cause poor performance but am consious it could occur on a high volume system.
Setting index statistics options for all databases >
sp_msforeachdb @command1='ALTER DATABASE ? SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS ON' sp_msforeachdb @command1='ALTER DATABASE ? SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS_ASYNC ON'
Sunday 26 August 2007
List SQL Instances on the network
c:\> osql -L
Only discovers servers that want to be found, i.e. where the SQL browser service is broadcasting their existance, and they are on the same subnet etc
Wednesday 22 August 2007
Login Failures : SSPI Errors
0x80090311 means "No authority could be contacted for authentication"
This is a Kerberos error and means the user cannot contact AD (active directory) to get a ticket.
Troubleshooting Kerberos Errors
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/windowsserver2003/technologies/security/tkerberr.mspx
SQL Server 2005 Remote Connectivity Issue TroubleShoot
http://blogs.msdn.com/sql_protocols/archive/2006/09/30/SQL-Server-2005-Remote-Connectivity-Issue-TroubleShooting.aspx
Tuesday 21 August 2007
Empty Database Script
This is primarily so I have a test database to use with Replication, Service Broker etc.
In this example I'm creating AdventureWorksTarget, an empty shell of the sample database for sql 2005.
1 Backup AdventureWorks
2 Restore as AdventureWorksTarget
3 Drop any views.
I'm adding this step as this is only a test, and the SCHEMABINDING option on the views preventing me from deleting from some tables.
Use this dynamic SQL to generate the sql, then run it >
SELECT 'DROP VIEW [' + S.name + '].[' + V.name + ']' FROM sys.views V JOIN sys.schemas S ON V.SCHEMA_ID = S.SCHEMA_ID
4 Create supporting procedures -
USP_DropXMLIndexes (code here)
USP_DropTableConstraints_2005 (code here)
5 Clear down XML Indexes and table constraints.
The order is important here, i.e -
1 Remove XML Indexes
2 Remove CHECK constraints
3 Remove FOREIGN KEY constraints
4 Remove PRIMARY KEY constraints
This dynamic sql calls the supporting procedures in the correct order.
Run it, then resulting sql it produces.
SELECT Command FROM ( SELECT Command = 'EXEC USP_DropXMLIndexes ''' + TABLE_SCHEMA + ''', ''' + TABLE_NAME + '''', 0 as SortOrder FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_CATALOG = 'AdventureWorksTarget' UNION SELECT Command = 'EXEC USP_DropTableConstraints_2005 ''' + TABLE_CATALOG + ''', ''' + TABLE_SCHEMA + ''', ''' + TABLE_NAME + ''', ''CHECK''', 1 as SortOrder FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_CATALOG = 'AdventureWorksTarget' UNION SELECT Command = 'EXEC USP_DropTableConstraints_2005 ''' + TABLE_CATALOG + ''', ''' + TABLE_SCHEMA + ''', ''' + TABLE_NAME + ''', ''FOREIGN KEY''', 2 as SortOrder FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_CATALOG = 'AdventureWorksTarget' UNION SELECT Command = 'EXEC USP_DropTableConstraints_2005 ''' + TABLE_CATALOG + ''', ''' + TABLE_SCHEMA + ''', ''' + TABLE_NAME + ''', ''PRIMARY KEY''', 3 as SortOrder FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_CATALOG = 'AdventureWorksTarget' ) CommandBlock ORDER BY SortOrder, Command
6 We can finally delete the data in all the tables -
EXECUTE sp_MSforeachtable 'TRUNCATE TABLE ?;'
Friday 17 August 2007
SQL 101 : SQL 2005 Schemas
‘User Schema Separation’ is allegedly an ANSI SQL 1999 standard but documentation on ansi standards is not freely available on the web.
2000 : [server].[database].[owner].object
2005 : [server].[database].[schema].object
Prior to SQL 2005, each database object had 1 owner.
In SQL Server terminology, the concept of a Schema was introduced in SQL 2005 to provide a logical way to group database objects, ease administration and address security.
| Database Structure | Organization Subdivide database into areas of interest / business area by assigning tables with schema names. For example in the AdventureWorks database > HumanResources.Employee Person.Address This is especially helpful in databases with a large number of tables, |
| Easier Assignment of permissions | Logical Permissions Grouping Permissions assigned at schema level make it easier to control relevant access to developers etc by subject area. Reduced Administration One command versus many when granting access to a set of objects when grouping them by schema. |
| Objects not reliant on users | Duplicate Objects In SQL 2000, objects being assigned to users means that 2 users could create objects with the same name which is confusing to say the least. Removing Users Objects not being directly tied to user accounts means that dropping user accounts is much easier. It can be accomplished without either dropping all the owned objects or changing the object owner for any linked objects. Users that OWN a schema now cannot be dropped however without changing the schema ownership. |
| Ease of teamworking | Multiple users can share a schema Multiple users can OWN a schema through a role or group membership. ‘Default Schema’ setting at user level prevents users having to explicitly reference a schema, for example – if they always use they same one. |
| Security | The addition of schemas means that combined with object permissions, many more levels of security can be achieved. Access to system objects can now be controlled by a user’s permissions on the SYS schema, unless of course their server role overrides this. |
| Script Order | Encompassing create statements for related objects inside the same schema makes scripting order unimportant. For example > CREATE SCHEMA UserInfo CREATE TABLE Logins ( UserId INT NOT NULL REFERENCES Users (UserId), LoginDate DATETIME ) CREATE TABLE Users ( UserId INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY )GO |
SQL 2000 / 2005 Underlying tables >
| | 2000 table | 2005 tables |
| Server level | syslogins | sys.server_principals |
| Database level | sysusers | sys.database_principals sys.schemas |
Wednesday 15 August 2007
Auditing Groups Membership from SQL Server
I have enhanced it to -
1) Not Error (the sql 2005 try/catch statements)
2) Utilise a table variable to store the results
3) Return a queryable recordset
Note :
This sql reveals accounts that are members of Windows group logins on this server.
It does not reveal group members in child domains or on other domains.
DECLARE @SqlGroupMembership TABLE(
ACCOUNT_NAME SYSNAME,
ACCOUNT_TYPE VARCHAR(30),
ACCOUNT_PRIVILEGE VARCHAR(30),
MAPPED_LOGIN_NAME SYSNAME,
PERMISSION_PATH SYSNAME
)
DECLARE @LoginName sysname
DECLARE cur_Loginfetch CURSOR FOR
SELECT [NAME] FROM master.sys.server_principals WHERE TYPE = 'G'
OPEN cur_Loginfetch
FETCH NEXT FROM cur_Loginfetch INTO @LoginName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
BEGIN TRY
-- Insert found users into table variable
INSERT INTO @SqlGroupMembership (ACCOUNT_NAME,ACCOUNT_TYPE,ACCOUNT_PRIVILEGE,MAPPED_LOGIN_NAME,PERMISSION_PATH)
EXEC xp_logininfo @LoginName , 'members'
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
-- Action for if insert fails
END CATCH
FETCH NEXT FROM cur_Loginfetch INTO @LoginName
END
CLOSE cur_Loginfetch
DEALLOCATE cur_Loginfetch
SELECT @@servername as servername,* FROM @SqlGroupMembership ORDER BY [PERMISSION_PATH], [ACCOUNT_NAME]
Saturday 4 August 2007
Moving tables to a new schema
-- Moving tables to a new schema -- step 1 - create the schema create schema [migration] -- step 2 - use sql to build the sql for tables to transfer select 'alter schema [migration] transfer dbo.' + name + ';' from sys.tables -- step 3 - run the sql generated by step 2
Thursday 2 August 2007
SQL 2005 : Granting multiple View Definitions
Useful for letting developers see what a proc does, without permissions to mess it up -
select 'GRANT VIEW DEFINITION ON [dbo].['+routine_name+'] TO [Domain\User]' from information_schema.routines where routine_type = 'procedure' --and routine_name like 'usp%'
Monday 30 July 2007
Adding / Dropping Users and Roles to multiple dbs
-- adding users and roles to multiple databases exec sp_msforeachdb @command1 ='use ? CREATE USER [domain\userorgroup] FOR LOGIN [domain\userorgroup] exec sp_addrolemember N''db_datareader'', N''domain\userorgroup''' -- dropping users and roles to multiple databases exec sp_msforeachdb @command1 ='use ? exec sp_droprolemember N''db_datareader'', N''domain\userorgroup'' DROP USER [domain\userorgroup]'
Saturday 28 July 2007
USP_DropXMLIndexes
e.g. EXEC USP_DropXMLIndexes 'Person', 'Contact'
CREATE PROCEDURE USP_DropXMLIndexes
@schemaname VARCHAR(128),
@tablename VARCHAR(128)
AS
-- USP_DropXMLIndexes by sql solace
DECLARE @sqlstring NVARCHAR(500)
WHILE EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM sys.internal_tables AS IT
JOIN sys.tables AS T
ON IT.PARENT_ID = T.OBJECT_ID
JOIN sys.schemas AS S
ON T.SCHEMA_ID = S.SCHEMA_ID
JOIN sys.xml_indexes AS XI
ON IT.PARENT_ID = XI.OBJECT_ID
AND IT.PARENT_MINOR_ID = XI.INDEX_ID
WHERE S.NAME = @schemaname
AND T.NAME = @tablename)
BEGIN
SELECT @sqlstring = 'DROP INDEX [' + XI.NAME + '] ON [' + S.NAME + '].[' + T.NAME + '] '
FROM sys.internal_tables AS IT
JOIN sys.tables AS T
ON IT.PARENT_ID = T.OBJECT_ID
JOIN sys.schemas AS S
ON T.SCHEMA_ID = S.SCHEMA_ID
JOIN sys.xml_indexes AS XI
ON IT.PARENT_ID = XI.OBJECT_ID
AND IT.PARENT_MINOR_ID = XI.INDEX_ID
WHERE S.NAME = @schemaname
AND T.NAME = @tablename
PRINT @sqlstring
EXECUTE sp_executesql @sqlstring
END
GO
Tuesday 17 July 2007
SQL Server 2005 Performance Dashboard Reports
A reports add-in for DBAs...
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyId=1d3a4a0d-7e0c-4730-8204-e419218c1efc&displaylang=en
Saturday 14 July 2007
2005 : XML Indexes
SELECT s.name as SchemaName, t.name as TableName, xi.name as XMLIndexName FROM sys.internal_tables AS it JOIN sys.tables AS t ON it.parent_id = t.object_id JOIN sys.schemas as s on t.schema_id = s.schema_id JOIN sys.xml_indexes AS xi ON it.parent_id = xi.object_id AND it.parent_minor_id = xi.index_id
Finding disabled XML Indexes
SELECT * FROM sys.xml_indexes WHERE is_disabled != 0;
Disabling an XML Index
ALTER INDEX indexname ON tablename DISABLE
Wednesday 11 July 2007
Disk Space Monitor - Further Scripts
Daily diskspace view -
create view ViewDailyDiskFree as select computer, drive, min(percentage) as percentage, CAST(FLOOR(CAST(Date AS float)) AS datetime) as dateoccurred, datediff(dd,date,getdate()) as daysago from tbldiskspace group by computer, drive, CAST(FLOOR(CAST(Date AS float)) AS datetime), datediff(dd,date,getdate())
SQL 7/2000 Cross-tab.
Uses 'case' statement and 'group by' to acheive cross-tab report >
select computer, drive, sum(case daysago when 6 then percentage else 0 end) as percentage_day_6, sum(case daysago when 5 then percentage else 0 end) as percentage_day_5, sum(case daysago when 4 then percentage else 0 end) as percentage_day_4, sum(case daysago when 3 then percentage else 0 end) as percentage_day_3, sum(case daysago when 2 then percentage else 0 end) as percentage_day_2, sum(case daysago when 1 then percentage else 0 end) as percentage_day_1, sum(case daysago when 0 then percentage else 0 end) as percentage_today from ViewDailyDiskFree group by computer, drive order by computer, drive
SQL 2005+ version
Uses PIVOT operator to achieve cross-tab report.
select computer, drive, isnull([6],0) as percentage_day_6, isnull([5],0) as percentage_day_5, isnull([4],0) as percentage_day_4, isnull([3],0) as percentage_day_3, isnull([2],0) as percentage_day_2, isnull([1],0) as percentage_day_1, isnull([0],0) as percentage_today from (select computer, drive, percentage , daysago from ViewDailyDiskFree) p pivot ( sum(percentage) for daysago in ([6],[5],[4],[3],[2],[1],[0]) ) as pivottable
Monday 9 July 2007
Disk Space Monitor
How to implement ...
- create a database for the project
- run the sql script to create the 3 tables in the new database
- populate tblSQLPhysicalServers manually with servernames to monitor
- edit .vbs script file to change the database connection parameters
- schedule the .vbs file to run using scheduled tasks in control panel (frequency as desired)
Table Schema Script -
-- table creation script CREATE TABLE [dbo].[tblSQLPhysicalServers] ( [servername] [nvarchar](50) ) GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[tblDiskSpaceLog]( [id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [notes] [varchar](1000) NULL, [date] [datetime] NULL DEFAULT (getdate()) ) GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[tblDiskSpace] ( [Computer] [varchar](128), [Drive] [varchar](2), [DiskSize] [decimal](28, 5) NULL, [FreeSpace] [decimal](28, 5) NULL, [Percentage] [decimal](10, 5) NULL, [Date] [datetime] NULL ) GO
VBS Script -
'***********************************************
'* *
'* Drive Monitor Script - save as a .vbs file *
'* *
'***********************************************
On Error Resume Next
Const intBytesPerMegabyte = 1048576
Dim AdCn
Dim AdRec
Dim strMonitorSQL, strSQL, strSQL2, strdate
Dim strServerName, strDataBase , strUsername, strPassword, strConnection
strServerName = "RIO\SQL2005"
strDataBase = "Monitor"
strUsername = "rd"
strPassword = "pass"
strConnection = "Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Data Source=" + strServerName + ";Initial Catalog=" + strDataBase + ";user id = '" + strUsername + "';password='" + strPassword + "' "
Function fnPadLeadingZero(intInputNumber, intTotalDigits)
If intTotalDigits > Len(intInputNumber) Then
fnPadLeadingZero = String(intTotalDigits -Len(intInputNumber),"0") & intInputNumber
Else
fnPadLeadingZero = intInputNumber
End If
End Function
Set AdCn = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
Set AdRec1 = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
Set AdRec2 = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
AdCn.Open = strConnection
strSQL = "Select ServerName from tblSQLPhysicalServers"
AdRec1.Open strSQL, AdCn,1,1
strMonitorSQL="insert into tblDiskSpaceLog(Notes) values ('Disk Monitoring - Started')"
AdRec2.Open strMonitorSQL, AdCn,1,1
'loop servers
While Not Adrec1.EOF
Computer = Adrec1("ServerName")
'connect to wmi for server
Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts://" & Computer)
'wscript.echo err.number
'check for wmi connection error
If err.number <> 0 Then
'wmi connection error
AdRec2.Open "insert into tblDiskSpaceLog(Notes) values ('Disk Monitoring - wmi error')", AdCn,1,1
strMonitorSQL="insert into tblDiskSpaceLog(Notes) values ('" + Computer + ": Error-- " + Err.description + "')"
AdRec2.Open strMonitorSQL, AdCn,1,1
Else
'wmi connected ok
Set colLogicalDisk = objWMIService.InstancesOf("Win32_LogicalDisk")
If err.number <> 0 Then
'cant connect to w32_logicaldisk
strMonitorSQL="insert into tblDiskSpaceLog(Notes) values ('" + Computer + ": Error-- " + Err.description+ "')"
AdRec2.Open strMonitorSQL, AdCn,1,1
Else
'w32_logicaldisk connected...
For Each objLogicalDisk In colLogicalDisk
If objLogicalDisk.drivetype=3 Then
strdate = YEAR(Date()) & "-" & fnPadLeadingZero(Month(Date()),2) & "-" & fnPadLeadingZero(DAY(Date()),2) & " " & time()
If objLogicalDisk.FreeSpace = "" Then
'freespace property empty
strSQL2 = "Insert into tblDiskSpace (Computer,Drive,DiskSize,date) values('"+Computer+"','" + objLogicalDisk.DeviceID + "'," + CInt(objLogicalDisk.size/intBytesPerMegabyte) + + ",'" + strdate + "')"
AdRec2.Open strSQL2, AdCn,1,1
Else
'freespace property given.
strSQL2 = "Insert into tblDiskSpace (Computer,Drive,DiskSize,FreeSpace,Percentage,date) values('"_
&Computer&"','" & objLogicalDisk.DeviceID &"',"& objLogicalDisk.size/intBytesPerMegabyte &_
"," & objLogicalDisk.freespace/intBytesPerMegabyte &_
"," &((objLogicalDisk.freespace/intBytesPerMegabyte)/(objLogicalDisk.size/intBytesPerMegabyte))*100_
&",'" & strdate &"')"
AdRec2.Open strSQL2, AdCn,1,1
If err.number <> 0 Then
wscript.echo err.description
End If
End If
'debug to see sql used for insert
'strMonitorSQL="insert into tblDiskSpaceLog(Notes) values ('" + replace(sql,"'","_")+ "')"
'AdRec2.Open strMonitorSQL, AdCn,1,1
End If
Next
End If
End If
err.Clear
Adrec1.movenext
Wend
AdRec2.Open "insert into tblDiskSpaceLog(Notes) values ('Disk Monitoring - Completed')", AdCn,1,1
Periodically review the recorded data e.g. within daily checks.
Use sql to query the tblDiskSpace table, like this -
SELECT Computer, Drive, DiskSize, FreeSpace, Percentage, Date FROM tblDiskSpace WHERE Dateadd(dd, -1,getdate()) < date AND Percentage < 25 ORDER BY Date DESC
(this query become a scheduled job itself)
Wednesday 4 July 2007
SSIS Configuration File
I had to hunt it down as after installing Integration Services the service would not start.
It turned out that it didnt like the fact that I have named instances of SQL 2005 (no default instance) and SSIS doesnt detect named instances by default.
Adding the instance name inside the servername tags sorted my problem.
Saturday 30 June 2007
CHECKSUM Table Synchronization
Prerequisites
1) Microsoft's Demo AdventureWorks database.
2) A second copy of AdventureWorks,, restored as AdventureSync
Step 1 : Create the usp_SyncTables procedure -
USE AdventureWorks GO CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.usp_SyncTables AS /**/ -- sync tables in tsql SET IDENTITY_INSERT [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] ON INSERT INTO [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] ([ContactID] ,[NameStyle] ,[Title] ,[FirstName] ,[MiddleName] ,[LastName] ,[Suffix] ,[EmailAddress] ,[EmailPromotion] ,[Phone] ,[PasswordHash] ,[PasswordSalt] ,[rowguid] ,[ModifiedDate]) SELECT source.[ContactID] ,source.[NameStyle] ,source.[Title] ,source.[FirstName] ,source.[MiddleName] ,source.[LastName] ,source.[Suffix] ,source.[EmailAddress] ,source.[EmailPromotion] ,source.[Phone] ,source.[PasswordHash] ,source.[PasswordSalt] ,source.[rowguid] ,source.[ModifiedDate] FROM [AdventureWorks].[Person].[Contact] source LEFT OUTER JOIN [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] target ON source.[ContactID] = target.[ContactID] WHERE target.[ContactID] is null SET IDENTITY_INSERT [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] OFF -- items to delete DELETE [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] FROM [AdventureWorks].[Person].[Contact] source RIGHT OUTER JOIN [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] target ON source.[ContactID] = target.[ContactID] WHERE source.[ContactID] is null -- items to update UPDATE [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] SET [NameStyle] = source.[NameStyle] ,[Title] = source.[Title] ,[FirstName] = source.[FirstName] ,[MiddleName] = source.[MiddleName] ,[LastName] = source.[LastName] ,[Suffix] = source.[Suffix] ,[EmailAddress] = source.[EmailAddress] ,[EmailPromotion] = source.[EmailPromotion] ,[Phone] = source.[Phone] ,[PasswordHash] = source.[PasswordHash] ,[PasswordSalt] = source.[PasswordSalt] ,[rowguid] = source.[rowguid] ,[ModifiedDate] = source.[ModifiedDate] from [AdventureWorks].[Person].[Contact] source join [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact] target on source.[ContactID] = target.[ContactID] and CHECKSUM(source.[NameStyle] ,source.[Title] ,source.[FirstName] ,source.[MiddleName] ,source.[LastName] ,source.[Suffix] ,source.[EmailAddress] ,source.[EmailPromotion] ,source.[Phone] ,source.[PasswordHash] ,source.[PasswordSalt] ,source.[rowguid] ,source.[ModifiedDate]) <> CHECKSUM(target.[NameStyle] ,target.[Title] ,target.[FirstName] ,target.[MiddleName] ,target.[LastName] ,target.[Suffix] ,target.[EmailAddress] ,target.[EmailPromotion] ,target.[Phone] ,target.[PasswordHash] ,target.[PasswordSalt] ,target.[rowguid] ,target.[ModifiedDate]) GO dbo.usp_SyncTables Procedure to update Person table from AdventureWorks For each table perform 3 operations > 1. Insert missing records 2. Remove deleted records 3. Update ammended records 1 20/05/2007 SQL Solace Original Version
Step 2 : Create some work for the sync procedure by messing up the data in the AdventureSync database -
-- Insert an extra 3770 rows in AdventureSync by duping rows where EmailPromotion = 2
INSERT INTO [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact]
([NameStyle]
,[Title]
,[FirstName]
,[MiddleName]
,[LastName]
,[Suffix]
,[EmailAddress]
,[EmailPromotion]
,[Phone]
,[PasswordHash]
,[PasswordSalt]
,[ModifiedDate])
SELECT [NameStyle]
,[Title]
,[FirstName]
,[MiddleName]
,[LastName]
,[Suffix]
,[EmailAddress]
,[EmailPromotion]
,[Phone]
,[PasswordHash]
,[PasswordSalt]
,[ModifiedDate]
FROM [AdventureWorks].[Person].[Contact]
WHERE [EmailPromotion] = 2
-- Update 468 rows
UPDATE [AdventureSync].[Person].[Contact]
SET [LastName] = 'Fred'
WHERE [LastName] LIKE 'Z%'
GO
Step 3 : Test the procedure -
use AdventureWorks; exec usp_SyncTables
The Output -
(0 row(s) affected)
(3770 row(s) affected)
(468 row(s) affected)
The output of the procedure shows -
0 rows inserted (correct, we didnt delete any)
3770 rows deleted (correct, these were the ones we inserted)
468 rows updated (correct, the LastName values have been corrected).
Friday 29 June 2007
Observation : SSIS Errors

All this is generated by a network failure >
- Copying to [Saved_Audit_Tables].[dbo].[PreCIS_WO_PAYMENT_CERTIFICATE_recalculation] (Error)
Messages
Error 0xc0202009: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_OLEDBERROR. An OLE DB error has occurred. Error code: 0x80004005.
An OLE DB record is available. Source: "Microsoft SQL Native Client" Hresult: 0x80004005 Description: "Protocol error in TDS stream".
An OLE DB record is available. Source: "Microsoft SQL Native Client" Hresult: 0x80004005 Description: "Protocol error in TDS stream".
An OLE DB record is available. Source: "Microsoft SQL Native Client" Hresult: 0x80004005 Description: "Communication link failure".
An OLE DB record is available. Source: "Microsoft SQL Native Client" Hresult: 0x80004005 Description: "TCP Provider: An existing connection was forcibly closed by the remote host.
".
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047038: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_PRIMEOUTPUTFAILED. The PrimeOutput method on component "Source 14 - WO_PAYMENT_CERTIFICATE_ReverseSTGMIgrationBefore" (2603) returned error code 0xC0202009. The component returned a failure code when the pipeline engine called PrimeOutput(). The meaning of the failure code is defined by the component, but the error is fatal and the pipeline stopped executing. There may be error messages posted before this with more information about the failure.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047021: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_THREADFAILED. Thread "SourceThread4" has exited with error code 0xC0047038. There may be error messages posted before this with more information on why the thread has exited.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047039: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_THREADCANCELLED. Thread "WorkThread3" received a shutdown signal and is terminating. The user requested a shutdown, or an error in another thread is causing the pipeline to shutdown. There may be error messages posted before this with more information on why the thread was cancelled.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047021: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_THREADFAILED. Thread "WorkThread3" has exited with error code 0xC0047039. There may be error messages posted before this with more information on why the thread has exited.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047039: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_THREADCANCELLED. Thread "WorkThread4" received a shutdown signal and is terminating. The user requested a shutdown, or an error in another thread is causing the pipeline to shutdown. There may be error messages posted before this with more information on why the thread was cancelled.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047021: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_THREADFAILED. Thread "WorkThread4" has exited with error code 0xC0047039. There may be error messages posted before this with more information on why the thread has exited.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc02020c4: Data Flow Task: The attempt to add a row to the Data Flow task buffer failed with error code 0xC0047020.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047038: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_PRIMEOUTPUTFAILED. The PrimeOutput method on component "Source 3 - PreCIS_WO_PAYMENT_CERTIFICATE" (115) returned error code 0xC02020C4. The component returned a failure code when the pipeline engine called PrimeOutput(). The meaning of the failure code is defined by the component, but the error is fatal and the pipeline stopped executing. There may be error messages posted before this with more information about the failure.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Error 0xc0047021: Data Flow Task: SSIS Error Code DTS_E_THREADFAILED. Thread "SourceThread3" has exited with error code 0xC0047038. There may be error messages posted before this with more information on why the thread has exited.
(SQL Server Import and Export Wizard)
Thursday 28 June 2007
CHECKSUM Column compatibility
Implicit conversion between XML types constrained by different XML schema collections is not allowed. Use the CONVERT function to run this query. "
I was comparing tables using CHECKSUM on the adventureworks database.
The Person.Contact table has a XML column which caused this (incompatible with CHECKSUM).
Column : AdditionalContactInfo
Datatype : xml(CONTENT Person.AdditionalContactInfoSchemaCollection)
Saturday 16 June 2007
AdminPak : Cool Remote Desktops Tool for XP
AdminPak for Windows XP -
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=c16ae515-c8f4-47ef-a1e4-a8dcbacff8e3&displaylang=en
Friday 15 June 2007
Creating and Enabling a CLR Function.
Prerequisite to this exercise > Enabling CLR Integration on SQL server.
Step 1 : Create a basic class in .NET -
- Start Visual Studio 2005
- File , New , Project
- Select 'Visual Basic' (left hand navigation pane) and 'Class Library' (right hand navigation pane).
- Select OK.

Way too much .net explanation would have to go here, but basic steps are >
- Name your class
- Name and code a function to be called from SQL (i've chosen a Roman Numerals one here).
- Save it!
- Give it a more sensible name -
Rename ClassLibrary1 to SQL_CLR_Project
(Do this in Solution Explorer on the right hand side) - File , Save All
Step 2 : Compile the class to a .DLL file >
Change Project properties -
- Project menu , SQL_CLR_Project Properties
- Change Assembly Name - I chose 'CLRFunctionLibrary' (This will match the .dll name i.e CLRFunctionLibrary.dll will be generated).
- Change the Root Name Space. I changed this to 'SQLCLROne' to match the project.
Compile it -
- Build Menu - 'Build SQLCLROne'

Find the dll just created (CLRFunctionLibrary.dll). -
C:\!RD\Visual Studio 2005\Projects\Class Libraries\SQLCLROne\ClassLibrary1\obj\Debug
Step 3 : Register the assembly within SQL Server -
In TSQL -
CREATE ASSEMBLY [CLRFunctionLibrary] FROM 'C:\!RD\Visual Studio 2005\Projects\Class Libraries\SQLCLROne\ClassLibrary1\bin\Debug\CLRFunctionLibrary.dll' WITH PERMISSION_SET = SAFE GO
These 2 queries verify the Assembly has been created, and will show other assemblies present -
SELECT * FROM sys.assemblies SELECT * FROM sys.assembly_files
Step 4: Register the method within the assembly. -
CREATE FUNCTION functionName (@sqlVariable AS sqlDataType) RETURNS sqlDataType AS EXTERNAL NAME Assembly.[NameSpace.ClassName].FunctionName
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.fn_RomanNumeral (@number AS INTEGER) RETURNS NVARCHAR(20) AS EXTERNAL NAME CLRFunctionLibrary.[SQLCLROne.SQLCLROne].RomanNumeral
Notes :
- I had to declare the Namespace when calling from the Assembly i.e the declaration became > CREATE FUNCTION functionName
- 2 Use the type of NVARCHAR not VARCHAR to match with the output STRING declared in vb.net.
(@sqlVariable AS sqlDataType)
RETURNS sqlDataType
AS EXTERNAL NAME Assembly.[NameSpace.ClassName].FunctionName
Now the function is created, you can see it like this -
SELECT * FROM sys.assembly_modules
and test it like this -
select dbo.fn_RomanNumeral(1066) select dbo.fn_RomanNumeral(1976) select dbo.fn_RomanNumeral(2007)
If you experience compatibility issues you can determine which version of .NET is installed by querying the sys.dm_os_loaded_modules DMV (dynamic management view).
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_os_loaded_modules WHERE [name] LIKE N'%\MSCOREE.DLL'
